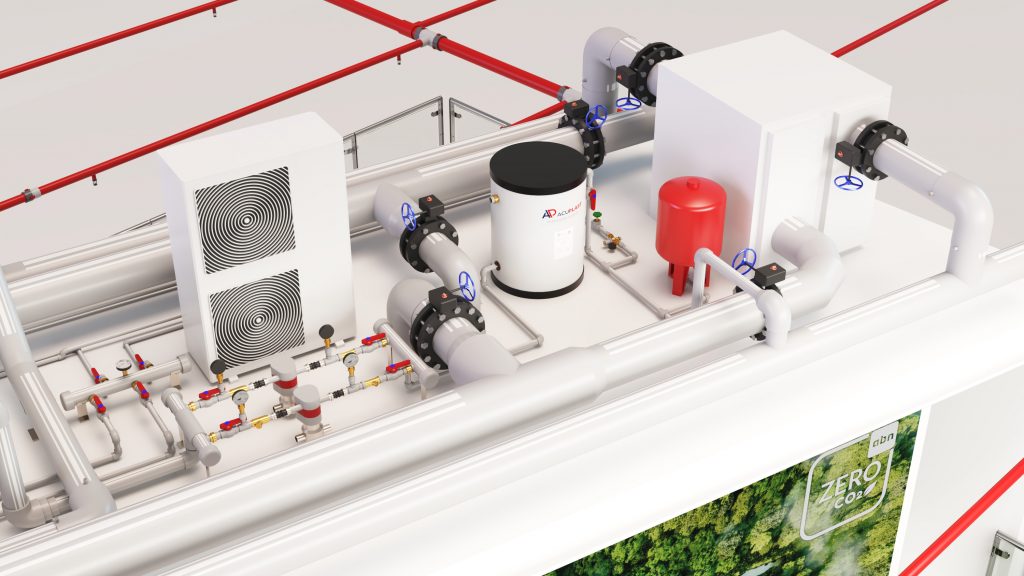
ABN pre-insulated pipes
Designing and manufacturing innovative systems that provide added value, guaranteeing a sustainable future.
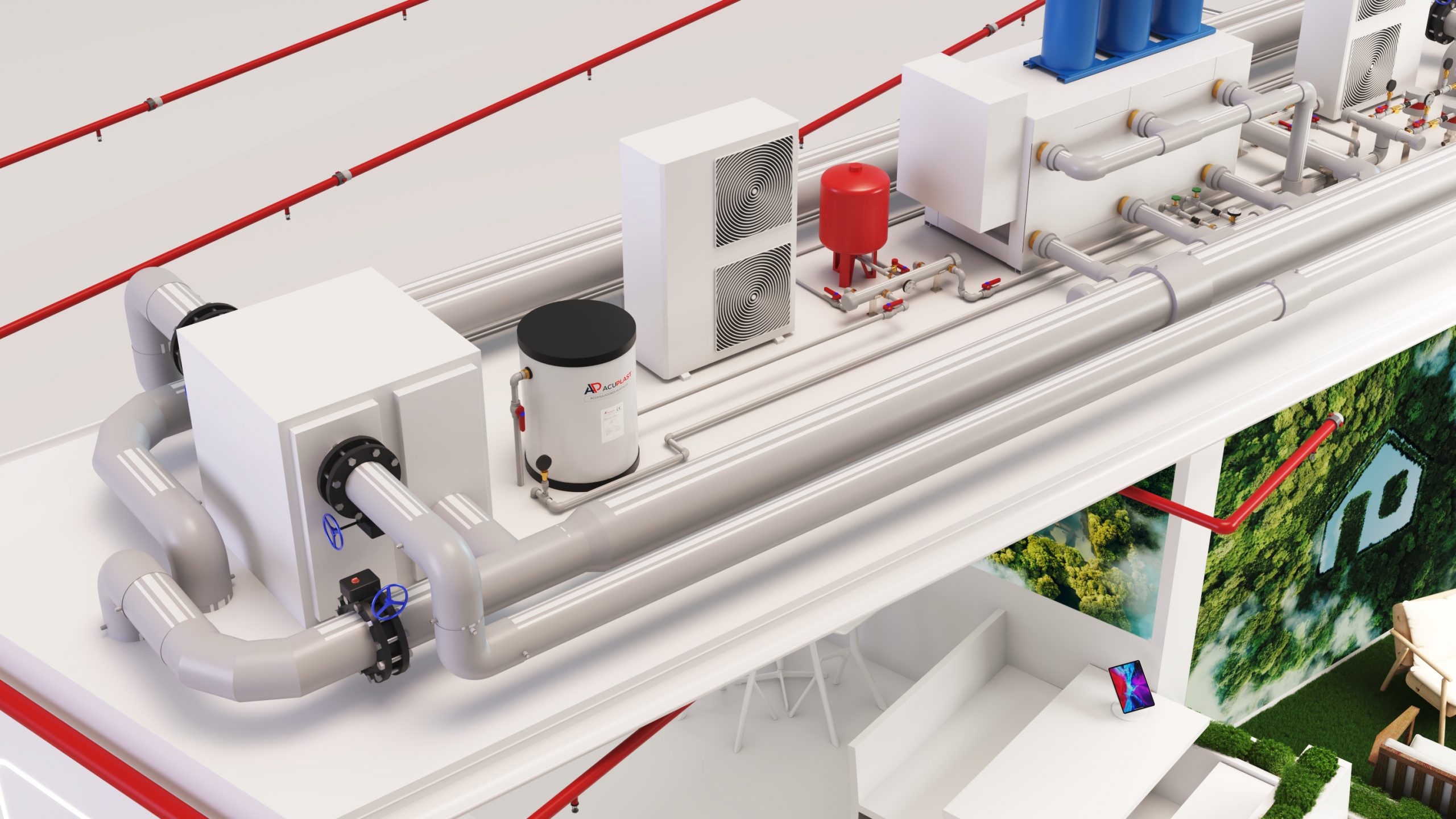

Pre-insulated piping systems
Pre-insulated polypropylene pipes are used to transport fluids through a piping system. They are designed with a thermal insulation coating on the outside and a polypropylene or polyethylene inner tube, which gives themexcellent chemical and thermal resistance.
These pipes are used in the distribution of hot and cold water, the transport of corrosive liquids, in air conditioning and district heating systems. The benefits of pre-insulated polypropylene pipes include their durability, their ability to resist high temperatures and pressures, their low maintenance cost and their energy efficiency, as insulation reduces heat losses in the piping system.
ABN Pipe Systems’ pre-insulated pipes contain PUR HFO foam and are composed of polyols of renewable origin from natural and recyclable oils, having a minimal environmental impact.

Pre-insulated pipe family
Main uses of pre-insulated pipes
ABN Pipe Systems’ pre-insulated pipes are versatile and efficient solutions designed for a wide variety of applications ensuring maximum energy efficiency and durability. These pipes are ideal for central heating systems, where their ability to minimise heat loss is crucial in maintaining optimum temperatures throughout extensive distribution networks. They are also perfect for district cooling networks, contributing to more sustainable and economical air-conditioning systems.
Our systems also excel in domestic hot water (DHW) and HVAC installations for commercial and residential buildings, providing a robust barrier against heat loss and condensation. Additionally, structural integrity and corrosion resistance make them ideal for underground and harsh environmental applications, such as those used in data centres, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
ABN// PPR CT INSU-PE
Heating and cooling distribution networks
Heating systems
District heating
Cooling systems
Data centres
Urban cooling
ABN// WATER INSU-PE
cold water distribution networks
Cooling systems
Urban cooling
Industrial cooling
Data centres
Benefits of pre-insulated pipes
ABN Pipe Systems’ pre-insulated pipes offer multiple technical and economic advantages, designed to exceed the expectations of the most demanding projects. Its high energy efficiency significantly reduces operating costs thanks to the exceptional insulation capacity of high-density polyurethane (PUR), which minimises heat losses and improves thermal performance throughout the entire system. In additional, corrosion resistance and UV protection ensure a long service life and reduced maintenance, ideal for installations in both indoor and outdoor environments.
These pipes also stand out for their sustainability, being fully recyclable products that support green buildings and contribute to obtaining environmental certifications for projects. Installation flexibility, with options adapted to buried, overhead or exposed installations, together with its compatibility with multiple joining systems (hot melt, electrofusion), facilitates its use in a variety of industrial and residential applications.
For projects requiring stringent technical specifications, our pre-insulated pipes comply with all relevant European standards, such as EN 253, providing a safe and effective solution. Explore how our pipes can optimise your next project by visiting our technical specifications and project gallery.
Labour savings
Space optimisation
Low thermal conductivity
Improving energy efficiency
UV protection
Corrosion resistance
Reduction of energy losses
Ecological and recyclable
Regulations: RITE, Reglamento de Instalaciones Térmicas de los Edificios
The RITE (Regulation of Thermal Installations in Buildings) is the regulation that governs the conditions that heating, air conditioning and domestic hot water installations, equipment and systems have to comply with, in order to achieve a rational use of energy, while at the same time satisfying the demand for thermal comfort and hygiene.
This regulation came into force in 2007, through Royal Decree 1027/2007 of 20 July 2007, and is therefore mandatory.
The sections included in the RITE include Technical Instruction IT1, where pipe insulation is considered.
TECHNICAL INSTRUCTION IT.1 DESIGN AND SIZING
IT 1.2.4.2 Pipe networks and ducts
IT 1.2.4.2.2.1 Thermal insulation of pipe networks
IT 1.2.4.2.2.1.1.1 General
- All pipes and fittings as well as equipment, appliances and tanks of thermal installations shall be provided with thermal insulation where they contain thermal insulation:
a) refrigerated fluids with a temperature lower than the ambient temperature of the room through which they flow;
b) fluids with a temperature higher than 40 ºC when installed in unheated premises, including corridors, galleries, walkways, car parks, machine rooms, false ceilings and raised floors, excluding cooling tower pipes and refrigeration compressor discharge pipes, except when they are within reach of persons.
Point 7 deals specifically with the calculation of the minimum insulation thickness, where either the simplified or the alternative procedure can be chosen. For installations above 70 kW the alternative method should be used.
- Simplified procedure A: in the simplified procedure the minimum thermal insulation thicknesses, expressed in mm, as a function of the outside diameter of the uninsulated pipe and the temperature of the fluid in the network and for a material with a reference thermal conductivity a 10ºC of 0,040 W/(m·K) must be those indicated in the relevant tables of the RITE.
| Outside diameter (mm) | Maximum fluid temperature (ºC) | ||
| 40…60 | >60…100 | >100…180 | |
| D ≤ 35 | 25 | 25 | 30 |
| 35 < D ≤ 60 | 30 | 30 | 40 |
| 60 < D ≤ 90 | 30 | 30 | 40 |
| 90 < D ≤ 140 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| 140 < D | 35 | 40 | 50 |
| Outside diameter (mm) | Maximum fluid temperature (ºC) | ||
| 40…60 | >60…100 | >100…180 | |
| D ≤ 35 | 35 | 35 | 40 |
| 35 < D ≤ 60 | 40 | 40 | 50 |
| 60 < D ≤ 90 | 40 | 40 | 50 |
| 90 < D ≤ 140 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| 140 < D | 45 | 50 | 60 |
| Outside diameter (mm) | Maximum fluid temperature (ºC) | ||
| >-10…0 | >0…10 | >10 | |
| D ≤ 35 | 30 | 25 | 20 |
| 35 < D ≤ 60 | 40 | 30 | 20 |
| 60 < D ≤ 90 | 40 | 30 | 30 |
| 90 < D ≤ 140 | 50 | 40 | 30 |
| 140 < D | 50 | 40 | 30 |
| Outside diameter (mm) | Maximum fluid temperature (ºC) | ||
| >-10…0 | >0…10 | >10 | |
| D ≤ 35 | 50 | 45 | 40 |
| 35 < D ≤ 60 | 60 | 50 | 40 |
| 60 < D ≤ 90 | 60 | 50 | 50 |
| 90 < D ≤ 140 | 70 | 60 | 50 |
| 140 < D | 70 | 60 | 50 |
- The minimum insulation thicknesses of pipe networks in continuous operation, such as domestic hot water networks, shall be those indicated in the tables above increased by 5 mm, as shown in the table below:
| O.D. (mm) | Insulation for DHW pipes | |
| Inside | Outside | |
| D ≤ 35 | 30 | 40 |
| 35 < D ≤ 60 | 35 | 45 |
| 60 < D ≤ 90 | 35 | 45 |
| 90 < D ≤ 140 | 45 | 55 |
| 140 < D | 45 | 55 |
- Simplified procedure B: when using materials with a thermal conductivity other than λref = 0,04 W/(m-K) at 10 °C, the determination of the minimum thickness is considered valid by applying the following equation:
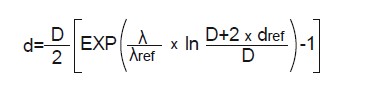
*where:
λref: reference thermal conductivity, equal to 0.04 W/(m-K) at 10 °C
λ: thermal conductivity of the material used, in W/(m-K) at 10 °C
dref: minimum reference thickness, mm
d: minimum thickness of material used, in mm
D: diameter inside of the insulating material, coinciding with the diameter outside of pipe, in mm.
ln: neperian logarithm (base 2.7183…)
EXP: means the neperian number raised to the expression in parenthesis
Download our ebook
Discover all about pre-insulated pipes: download our free eBook now and dive into the world of advanced piping system solutions. Your complete guide awaits!



